What is Layer Height in 3D Printing? A Deep Dive into the Details
3D printing has revolutionized modern manufacturing, prototyping, and even hobbyist design. From intricate jewelry to large-scale mechanical parts, 3D printing allows creators to bring digital designs to life with precision and customization. Among the many parameters that determine the quality and characteristics of a 3D-printed object, layer height stands out as one of the most critical.
But what exactly is layer height, and why does it matter?
Let’s dive deep into the concept, benefits, challenges, and how selecting the right layer height can significantly impact your 3D print outcomes.
Understanding Layer Height in 3D Printing
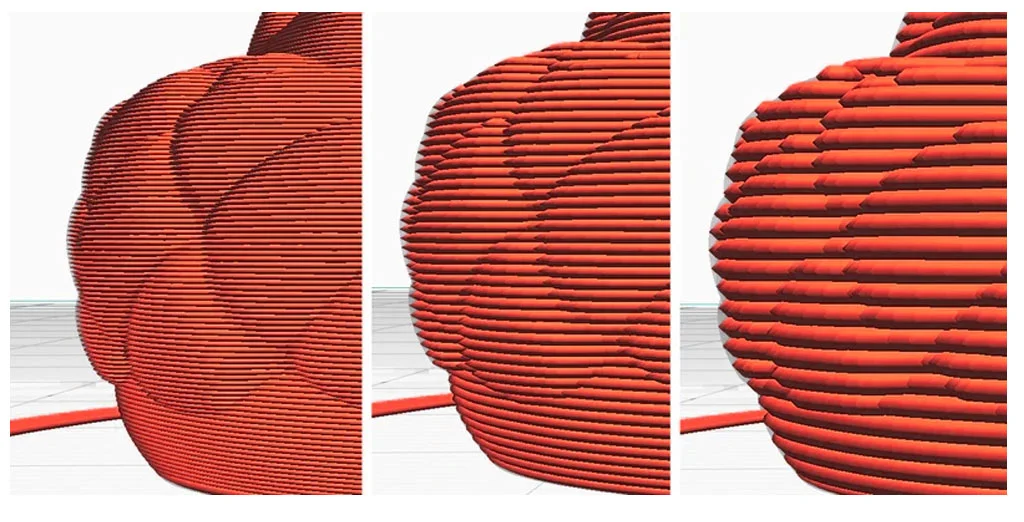
In 3D printing, objects are built layer by layer. Each layer is deposited by the 3D printer’s nozzle (in FDM printing) or formed by light (in SLA or resin printing). Layer height, also referred to as print resolution or z-resolution, is the thickness of each of these layers.
Layer height is typically measured in microns (µm) or millimeters (mm). For example:
A layer height of 0.1 mm (100 microns) means each printed layer is 0.1 mm tall.
A layer height of 0.3 mm (300 microns) means thicker, more visible layers.
The smaller the layer height, the higher the resolution and more detailed the final object will appear. Conversely, larger layer heights lead to faster prints but lower surface quality.
How Layer Height Affects 3D Prints
Let’s break down how different layer heights influence your print outcomes:
1. Print Quality
Lower layer heights (0.1 mm or less) produce smoother surfaces and more detailed features. Ideal for figurines, miniatures, and high-detail prototypes.
Higher layer heights (0.2 mm – 0.3 mm) result in more visible layer lines. These are suitable for mechanical parts where aesthetics are less important.
2. Print Time
Lower layer heights significantly increase print time because the printer must complete more layers.
Higher layer heights reduce print time, making them ideal for drafts, test prints, or functional parts where precision is not critical.
3. Strength and Durability
Thicker layers can lead to stronger prints in the Z-axis because of better interlayer bonding.
However, this also depends on other factors like infill density and material type.
4. Material Usage
Layer height doesn’t directly affect the total volume of material used, but finer layers may require more retractions and movements, potentially leading to more waste or stringing in FDM printing.
Choosing the Right Layer Height: A Practical Guide
Selecting the right layer height depends on the purpose of the print and the desired balance between speed, quality, and strength.
Common Use Cases:
| Application | Recommended Layer Height |
|---|---|
| Detailed Miniatures | 0.05 mm – 0.1 mm |
| Prototypes with Functional Fit | 0.1 mm – 0.2 mm |
| Mechanical Parts | 0.2 mm – 0.3 mm |
| Large Models/Prototypes | 0.3 mm+ |
Pro Tip: Many printers perform optimally at layer heights that are multiples of the nozzle size. For example, with a 0.4 mm nozzle, common layer heights are 0.12 mm, 0.16 mm, 0.2 mm, etc.
The Impact of Layer Height on Different 3D Printing Technologies
Layer height behaves differently across various 3D printing technologies:
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling)
Most common desktop 3D printing method.
Layer heights typically range from 0.05 mm to 0.3 mm.
Ideal for functional parts, engineering components, or rapid prototyping.
SLA (Stereolithography) and DLP
Uses light to cure resin in layers.
Achieves much finer resolutions, often as low as 0.025 mm.
Best suited for highly detailed objects like dental models, jewelry, or figurines.
SLS (Selective Laser Sintering)
Uses a laser to fuse powder material.
Has a different surface finish and doesn’t produce visible layer lines.
Layer height usually ranges from 0.1 mm to 0.12 mm.
Advantages of Using Fine Layer Heights
While fine layers take more time, they bring significant advantages:
Exceptional Detail – Ideal for models requiring a high level of realism or intricate patterns.
Smooth Finish – Reduces the need for post-processing or sanding.
Better Fit for Moving Parts – More precise tolerances.
Disadvantages of Using Very Low Layer Heights
However, using ultra-fine layer heights comes with trade-offs:
Increased Print Time – A part that takes 3 hours at 0.2 mm could take 9+ hours at 0.1 mm.
Higher Risk of Print Failure – More layers mean more chances something could go wrong mid-print.
May Not Add Visible Benefit – On some models, the visual difference is minimal and not worth the extra time.
Optimizing Layer Height for Professional and Commercial Use
When working on commercial or client projects, selecting the optimal layer height is part of delivering quality and efficiency. Businesses need to consider:
Client expectations for detail and surface finish.
The project timeline.
Cost efficiency in material and labor.
Intended application (aesthetic model vs. functional prototype).
At DigiGlen, we help businesses make these decisions with expert consultation and access to cutting-edge 3D printing technologies.
Why Choose DigiGlen for Your 3D Printing Needs?
At DigiGlen, we don’t just print models—we craft experiences and deliver solutions.
Here’s why we’re the preferred 3D printing partner for designers, engineers, educators, and entrepreneurs:
✅ Expert Guidance
We help you choose the perfect layer height and material based on your application. Whether you need ultra-detailed prints or rapid prototyping, we’ve got you covered.
✅ Advanced Equipment
We use a range of industrial-grade FDM, SLA, and SLS machines, ensuring precision, reliability, and efficiency across all projects.
✅ Speed + Quality
Our process optimizes print time vs. quality, so you get fast turnaround without sacrificing performance.
✅ Quality Control
Every print goes through rigorous inspection, so what you get is exactly what you expect—or better.
✅ End-to-End Services
From CAD design to prototyping to batch manufacturing, we offer complete 3D solutions under one roof.
✅ Eco-Friendly Options
We offer sustainable materials and waste-reducing techniques, helping you meet environmental goals.
Conclusion: Layer Height is More Than Just a Number
Layer height in 3D printing is a pivotal setting that affects quality, speed, strength, and cost. Whether you’re a hobbyist printing your next cosplay piece or a product engineer developing the next big thing, understanding and optimizing layer height is key to success.
The right balance depends on your specific needs, and that’s where DigiGlen comes in. With our expertise and equipment, we ensure your projects are printed with precision, care, and efficiency.
Ready to Print Your Vision?
Choose DigiGlen for reliable, high-quality, and tailored 3D printing solutions. Let us help you bring your ideas to life—layer by layer.
Recent Comments
Post Widget
How to Choose the Best 3D Printing Filament: A Complete Guide
What is Layer Height in 3D Printing?
Mastering 3D Print Post-Production
Social Media Widget
Customer service
It’s not actually free we just price it into the products.

Fast Free Shipping
Get free shipping on orders of $150 or more
(within the US)

Returns & Exchanges
We offer free returns and exchanges within 30 days of purchase.

Secure payment
Your payment information is processed securely and encrypted.